CommunityNews
Inside the Universe Machine: The Webb Space Telescope’s Ultra-Reliable Radio

When the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) reveals its first images on 12 July, they will be the byproduct of carefully crafted mirrors and scientific instruments. But all of its data-collecting prowess would be moot without the spacecraft’s communications subsystem.
The Webb’s comms aren’t flashy. Rather, the data and communication systems are designed to be incredibly, unquestionably dependable and reliable. And while some aspects of it are relatively new—it’s the first mission to use Ka-band frequencies for such high data rates so far from Earth, for example—above all else, JWST’s comms provide the foundation upon which JWST’s scientific endeavors sit.
As previous articles in this series have noted, JWST is parked at Lagrange point L2. It’s a point of gravitational equilibrium located about 1.5 million kilometers beyond Earth on a straight line between the planet and the sun. It’s an ideal location for JWST to observe the universe without obstruction and with minimal orbital adjustments.
Being so far away from Earth, however, means that data has farther to travel to make it back in one piece. It also means the communications subsystem needs to be reliable, because the prospect of a repair mission being sent to address a problem is, for the near term at least, highly unlikely. Given the cost and time involved, says Michael Menzel, the mission systems engineer for JWST, “I would not encourage a rendezvous and servicing mission unless something went wildly wrong.”
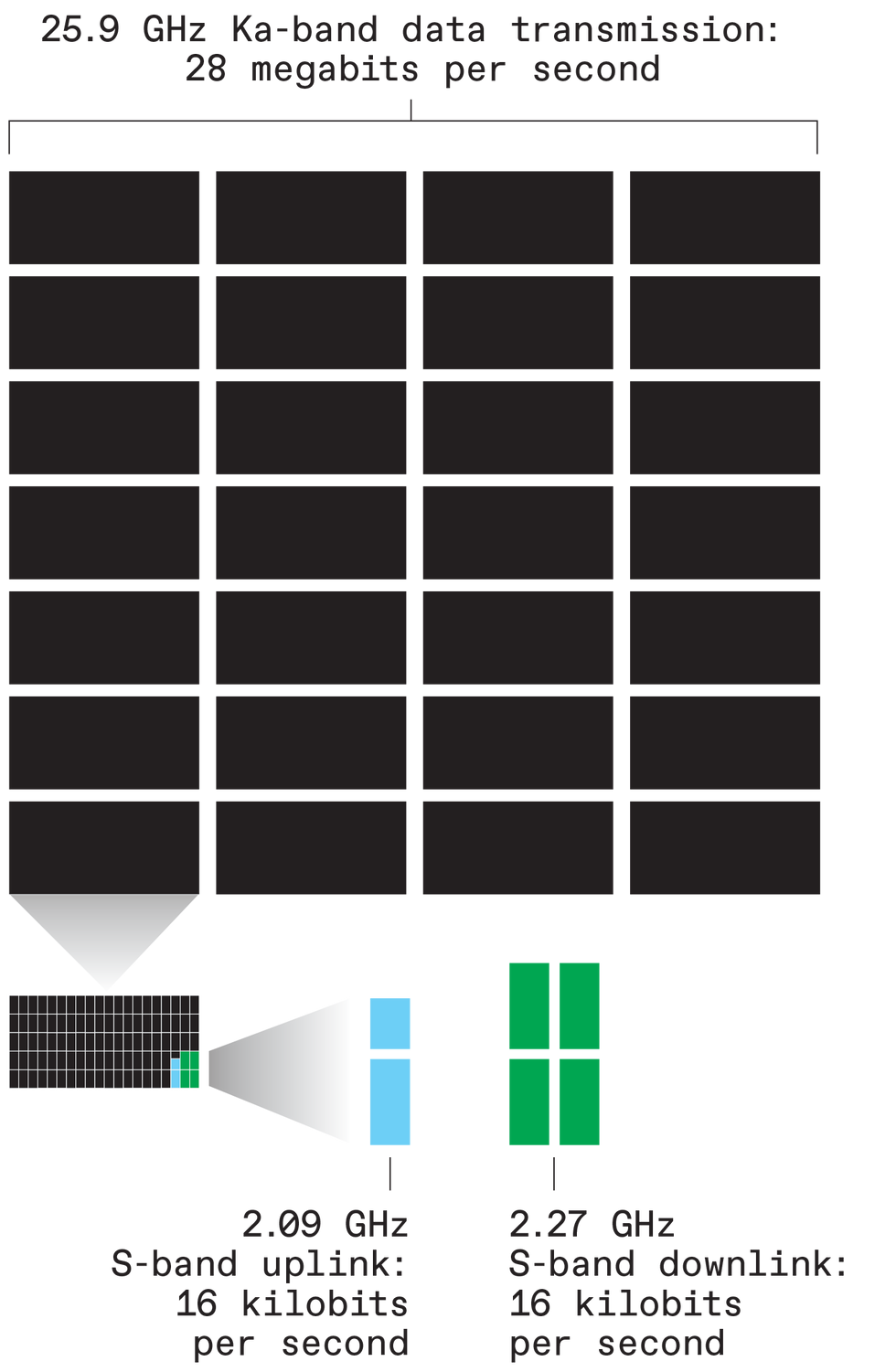
According to Menzel, who has worked on JWST in some capacity for over 20 years, the plan has always been to use well-understood Ka-band frequencies for the bulky transmissions of scientific data. Specifically, JWST is transmitting data back to Earth on a 25.9 gigahertz channel at up to 28 megabits per second. The Ka-band is a portion of the broader K-band (Another portion, the Ku-band, was also considered).

The Lagrange points are equilibria locations where competing gravitational tugs on an object net out to zero. JWST is one of two other craft currently occupying L2. IEEE Spectrum
Both the data collection and transmission rates of JWST dwarf the older Hubble Space Telescope. Compared to Hubble, which is still active and generates 1 to 2 gigabytes of data daily, JWST can produce up to 57 GB each day (although that amount is dependent on what observations are scheduled).
Menzel says he first saw the frequency selection proposals for JWST around 2000, when he was working at Northrop Grumman. He became the mission systems engineer in 2004. “I knew where the risks were in this mission. And I wanted to make sure that we didn’t get any new risks,” he says.

IEEE Spectrum
Besides, Ka-band frequencies can transmit more data than X-band (7 to 11.2 GHz) or S-band (2 to 4 GHz), common choices for craft in deep space. A high data rate is a necessity for the scientific work JWST will be undertaking. In addition, according to Carl Hansen, a flight systems engineer at the Space Telescope Science Institute (the science operations center for JWST), a comparable X-band antenna would be so large that the spacecraft would have trouble remaining steady for imaging.
Although the 25.9 GHz Ka-band frequency is the telescope’s workhorse communication channel, it also employs two channels in the S-band. One is the 2.09 GHz uplink that ferries future transmission and scientific observation schedules to the telescope at 16 kilobits per second. The other is the 2.27 GHz, 40 kbps downlink over which the telescope transmits engineering data—things including its operational status, systems health, and other information concerning the telescope’s day to day activities.
Any scientific data the JWST collects during its lifetime will need to be stored on board, because the spacecraft doesn’t maintain round-the-clock contact with Earth. Data gathered from its scientific instruments, once collected, is stored within the spacecraft’s 68-gigabyte solid state drive (3 percent is reserved for engineering and telemetry data). Alex Hunter, also a flight systems engineer at the Space Telescope Science Institute, says that by the end of JWST’s 10-year mission life, they expect to be down to about 60 GB because of deep space radiation and wear and tear.
The on-board storage is enough to collect data for about 24 hours before it runs out of room. Well before that becomes an issue, JWST will have scheduled opportunities to beam that invaluable data to Earth.
JWST will stay connected via the Deep Space Network (DSN)—a resource it shares with the Parker Solar Probe, Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite, the Voyager probes, and the entire ensemble of Mars rovers and orbiters, to name just a few of the other heavyweights. The DSN consists of three antenna complexes: Canberra, Australia; Madrid, Spain; and Barstow, California. JWST needs to share finite antenna time with plenty of other deep space missions, each with unique communications needs and schedules.
IEEE Spectrum
Sandy Kwan, a DSN systems engineer, says that contact windows with spacecraft are scheduled 12 to 20 weeks in advance. JWST had a greater number of scheduled contact windows during its commissioning phase, as instruments were brought online, checked, and calibrated. Most of that process required real-time communication with Earth.
All of the communications channels use the Reed-Solomon error correction protocol—the same error-correction standard as used in DVDs and Blu-ray discs as well as QR codes. The lower data rate S-band channels use binary phase shift key modulation—involving phase shifting of a signal’s carrier wave. The K-band channel, however, uses a quadrature phase shift key modulation. Quadrature phase shift keying can double a channel’s data rate, at the cost of more complicated transmitters and receivers.
JWST’s communications with Earth incorporate an acknowledgement protocol—only after the JWST gets confirmation that a file has been successfully received will it go ahead and delete its copy of the data to clear up space.
The communications subsystem was assembled along with the rest of the spacecraft bus by Northrop Grumman, using off-the-shelf components sourced from multiple manufacturers.
JWST has had a long and often-delayed development, but its communications system has always been a bedrock for the rest of the project. Keeping at least one system dependable means it’s one less thing to worry about. Menzel can remember, for instance, ideas for laser-based optical systems that were invariably rejected. “I can count at least two times where I had been approached by people who wanted to experiment with optical communications,” says Menzel. “Each time they came to me, I sent them away with the old, ‘Thank you, but I don’t need it. And I don’t want it.’”
Read in full here:
This thread was posted by one of our members via one of our news source trackers.
Popular Science Tech topics

Other popular topics

Categories:
Sub Categories:
Popular Portals
- /elixir
- /rust
- /wasm
- /ruby
- /erlang
- /phoenix
- /keyboards
- /python
- /js
- /rails
- /security
- /go
- /swift
- /vim
- /clojure
- /java
- /emacs
- /haskell
- /svelte
- /typescript
- /onivim
- /kotlin
- /c-plus-plus
- /crystal
- /tailwind
- /react
- /gleam
- /ocaml
- /flutter
- /elm
- /vscode
- /ash
- /html
- /opensuse
- /zig
- /centos
- /deepseek
- /php
- /scala
- /react-native
- /lisp
- /textmate
- /sublime-text
- /nixos
- /debian
- /agda
- /django
- /deno
- /kubuntu
- /arch-linux
- /nodejs
- /revery
- /ubuntu
- /manjaro
- /spring
- /julia
- /diversity
- /lua
- /markdown
- /c










